When it comes to audio production, every detail matters. The quality of your audio cables can significantly affect the sound you capture. In this article, we’ll explore the difference between balanced and unbalanced audio cables, helping you make informed choices for your audio setup.
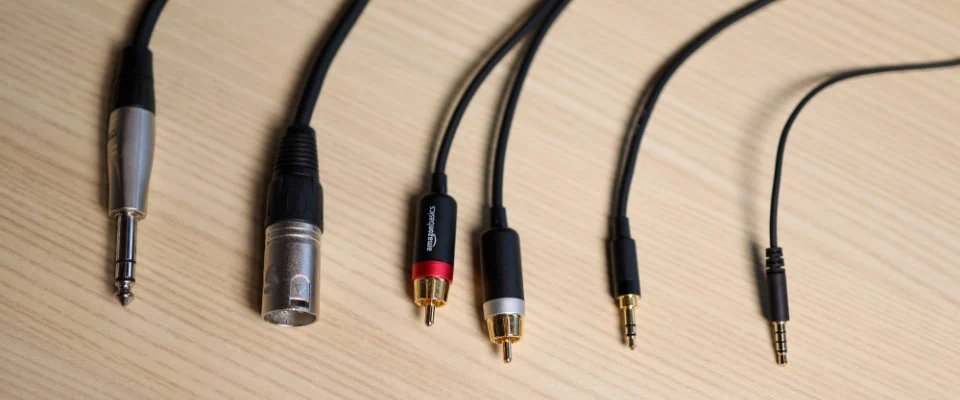

Understanding Balanced and Unbalanced Audio
Audio cables can be categorized into two types: balanced and unbalanced. The primary distinction lies in their susceptibility to unwanted noise and interference. Balanced audio cables provide a stronger, cleaner audio signal, while unbalanced cables are more prone to noise.
The Structure and Function of Unbalanced Audio
Unbalanced audio cables consist of two wires: a signal wire and a ground wire. The signal wire carries the audio signal, while the ground wire acts as a reference point. However, the ground wire can also function as an antenna, picking up unwanted noise during transmission.
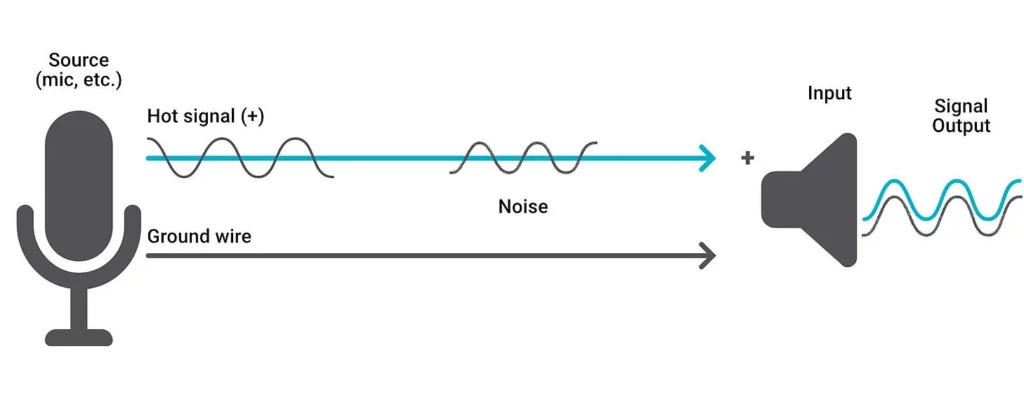
Sources of Noise in Unbalanced Cables
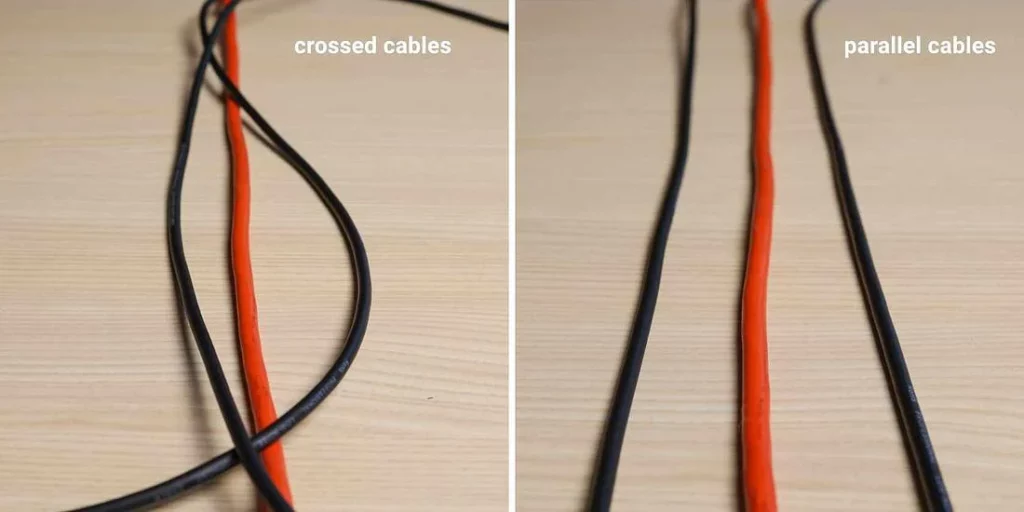
Unbalanced cables can pick up noise from various sources, including electrical and radio interferences. Power cables, especially non-LED stage lighting, are common culprits. When unbalanced cables run parallel to power cables, they are more susceptible to signal interference and humming sounds.
Reducing Noise in Unbalanced Cable Setup
To minimize the noise in unbalanced cable setups, it is essential to be mindful of cable placement. Whenever possible, avoid running audio and power cables in parallel. If parallel runs are unavoidable, maximize the distance between audio and power cables to minimize interference.
Types of Unbalanced Cables
RCA Cables
RCA cables are widely used for unbalanced analog audio connections. They typically consist of a red tip (right channel) and a white or black tip (left channel). RCA unbalanced signals are best suited for shorter distances, usually not exceeding 25 feet.

Quarter-Inch TS Cables
Quarter-inch TS (tip, sleeve) cables are commonly used for unbalanced signals, particularly with electric guitars connecting to amplifiers. These cables provide a straightforward connection and are ideal for short-distance applications.
What is Balanced Audio
Balanced audio cables share similarities with unbalanced cables but include an additional component: the ground wire. In addition to the signal wire, balanced cables carry two copies of the same audio signal—one positive (hot) and one negative (cold).
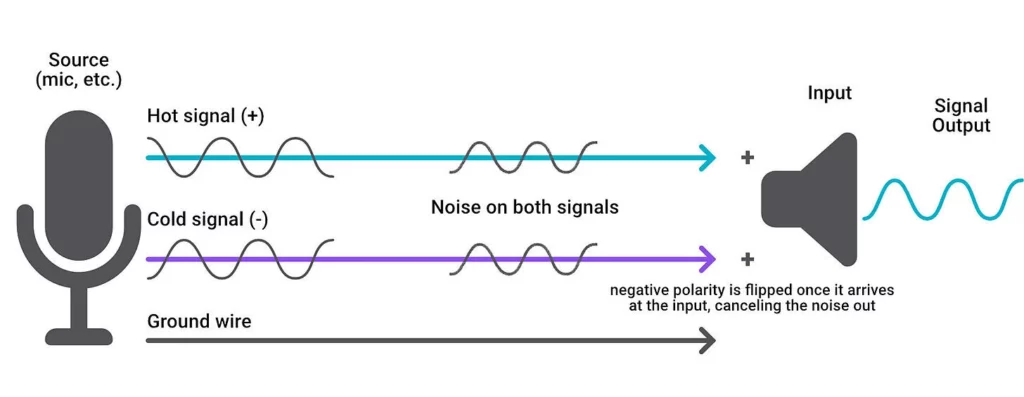
The Hot and Cold Signals in Balanced Cables
In balanced audio cables, the hot and cold signals have opposite polarities. As these signals travel along the cable, they cancel each other out. However, when they reach the end of the cable, the polarity of the cold signal flips, aligning both signals in phase and perfectly synchronized.
Common-Mode Rejection in Balanced Cables
One of the significant advantages of balanced audio cables is their ability to reject common-mode noise. Any noise picked up along the cable affects both the hot and cold signals, but when the signals are combined at the receiving end, the noise cancels out. This rejection of noise is known as common-mode rejection.
Benefits of Balanced Signals
Balanced audio signals offer several benefits over unbalanced signals. They provide a stronger, cleaner audio signal with significantly reduced noise and interference. Balanced signals are also louder, delivering approximately 6-10 dB more volume compared to unbalanced signals.
Types of Balanced Cables
XLR Cables
XLR cables are commonly used for balanced audio signals, especially in professional audio setups. These cables consist of three male pins inside the connector: the ground wire, the hot signal, and the cold signal. XLR cables can transmit balanced audio signals up to 200 feet.
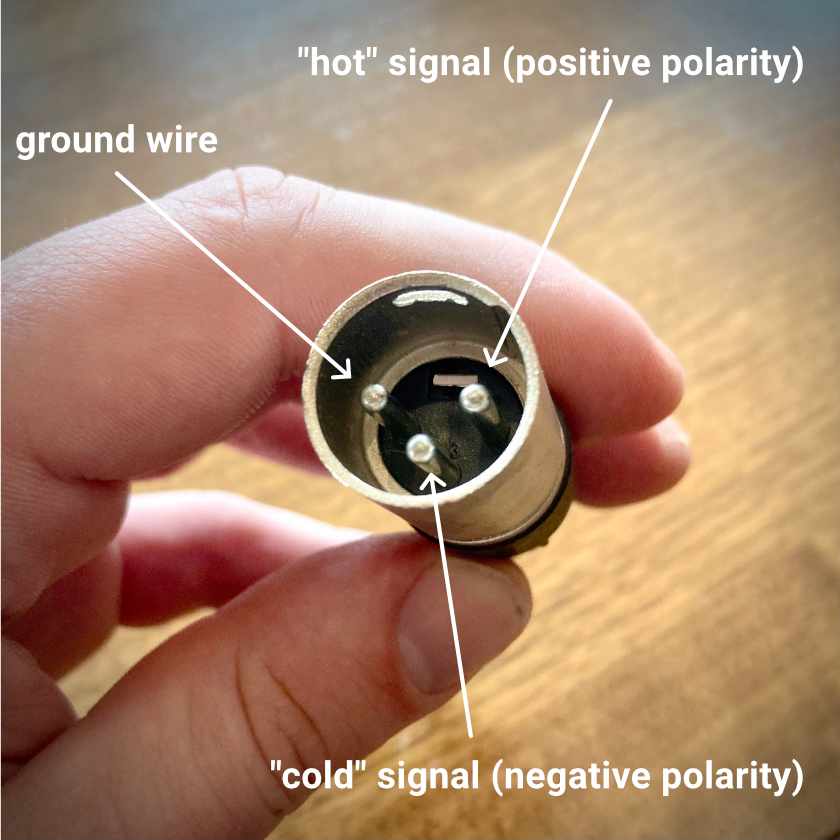

Quarter-Inch TRS Cables
Quarter-inch TRS (tip, ring, sleeve) cables are another type of balanced professional audio cable. They can transmit either mono (balanced) or stereo (unbalanced) signals. The structure of a quarter-inch TRS cable allows for balanced audio transmission and is commonly used in various audio applications.
Choosing Between Balanced and Unbalanced Cables
When deciding between balanced and unbalanced cables, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of your audio setup. Unbalanced cables are suitable for short distances and lower-budget setups where the risk of distortion is minimal. Balanced cables are ideal for longer distances, professional audio applications, and environments with higher susceptibility to noise.
Common Misconceptions about Balanced Audio
There is a common misconception that balanced audio signals refer to left/right stereo balance. However, balanced audio cables can carry either balanced or unbalanced stereo signals. It’s crucial to understand the difference between balanced/unbalanced signals and balanced/unbalanced cables to make informed choices.
Conclusion
The choice between balanced and unbalanced audio cables is vital to achieving high-quality sound in your audio production. Balanced cables offer superior noise rejection, cleaner signals, and increased volume levels. Unbalanced cables, while more susceptible to noise, can be cost-effective for shorter distances and certain setups. By understanding the differences between these two types of cables, you can make informed decisions that improve your audio quality and meet your specific needs.
47,673 total views, 35 views today

Pauline is a Marketing Specialist at YoloLiv, with over three years of experience in overseas digital marketing. She aims to produce high-quality and practical content for all tech lovers and dig deeper into the live streaming fields.

